Luke Skywalker
Super Moderator
{vb:raw ozzmodz_postquote}:
Get the news
Log In or Subscribe to skip
[h=6]Share This Story![/h]Let friends in your social network know what you are reading about
[h=4]Hubble breaks cosmic distance record, spots oldest galaxy ever found[/h]NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has discovered a galaxy far, far away.<span style="color: Red;">*</span>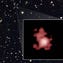
{# #}
[h=4]Sent![/h]A link has been sent to your friend's email address.
[h=4]Posted![/h]A link has been posted to your Facebook feed.
[h=6]Join the Nation's Conversation[/h]To find out more about Facebook commenting please read the Conversation Guidelines and FAQs
[h=2]UP NEXT[/h][h=2]03[/h]
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope is celebrating its 25th anniversary of being placed into orbit. NASA unveiled the official Hubble anniversary image to mark the occasion. (April 23) AP
NASA announced Thursday that researchers had successfully smashed the cosmic distance record by spotting the bright infant galaxy, named GN-z11.(Photo: NASA, ESA, and G. Bacon (STScI))
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has discovered a galaxy far, far away.
So far, in fact, that it is the farthest galaxy ever seen in the universe.<span style="color: Red;">*</span>NASA announced Thursday that researchers had successfully smashed the cosmic distance record by spotting the bright infant galaxy, named GN-z11.
Images show the galaxy how it appeared<span style="color: Red;">*</span>13.4 billion years in the past, just 400 million years after the Big Bang, according to a statement from NASA.
The images offer a sneak peak at the past and are one step closer to allowing researchers to see the first galaxies that formed the universe, according to<span style="color: Red;">*</span>Patrick McCarthy, interim president of the Giant Magellan Telescope Organization.
“One of the Holy Grails of astronomy is to look back to see the first galaxies and, of course, stars when they formed,” <span style="color: Red;">*</span>McCarthy said in a phone interview. "This discovery really pushes back the frontier further than we expected.”
So, how were researchers able to see a galaxy from so long ago?
USA TODAY
Hubble captures image of 'blue bubble' in space
The light emitted from far-off galaxies takes time<span style="color: Red;">*</span>to reach our telescopes and cameras, so<span style="color: Red;">*</span>the further the galaxy, the further back in time we see,<span style="color: Red;">*</span>McCarthy said.<span style="color: Red;">*</span>When you take a picture of a<span style="color: Red;">*</span>star that is one<span style="color: Red;">*</span>light-year away, you are seeing that star as it appeared one year in the past, he said.
"Seeing a picture of a galaxy<span style="color: Red;">*</span>when it was<span style="color: Red;">*</span>younger or all the way back to the Big Bang 13-billion-years-away,<span style="color: Red;">*</span>that light has traveled a long way," he said.<span style="color: Red;">*</span>"It's<span style="color: Red;">*</span>like digging up a fossil, you see what life was like millions of years ago, it’s almost a fossil of the early universe."
For galaxies that are billions of years away,<span style="color: Red;">*</span>astronomers can measure the distance to a galaxy by measuring its “redshift,” which is caused by the expansion of the universe, according to NASA.
“Every distant object in the universe appears to be receding from us because its light is stretched to longer, redder wavelengths as it travels through expanding space to reach our telescopes,” according to NASA.
When the “redshifted” light from these distant galaxies makes its way close enough for our telescope to capture, the information from the light allows researchers to see the galaxies as they were billions of years ago.
“We’ve taken a major step back in time, beyond what we’d ever expected to be able to do with Hubble,” Pascal Oesch of Yale University said in a statement. <span style="color: Red;">*</span>“We see GN-z11 at a time when the universe was only three percent of its current age.”
Hubble was pushed to the "limits" to observe the distant galaxy, and NASA researchers believe the telescope will hold the cosmic distance record until the James Webb Space Telescope is launched into space in 2018.<span style="color: Red;">*</span>Before GN-z11 the farthest galaxy ever measured was 13.2 billion years in the past.
McCarthy said the discovery is another step forward in the quest to "explore the beginning of the universe<span style="color: Red;">*</span>and the<span style="color: Red;">*</span>cosmic dawn, the time when the<span style="color: Red;">*</span>universe went form dark to lit up."
Gallery: History and images of Hubble Space Telescope
Follow @MaryBowerman on Twitter.<span style="color: Red;">*</span>
0) { %> 0) { %>
0) { %>
Powered By WizardRSS.com | Full Text RSS Feed
